Executive Summary
Our world has shrunk, our pace of life has become frenetic, our work-life more demanding, and businesses have globalized. We live in the age of “instant gratification” – everything has to be faster, cheaper, better.
In such a scenario, the Logistics and Supply Chain industry has come under severe pressure to keep up with the rapidly increasing demands of Customers and Consumers. From the old “out for delivery” that was sufficient we now want “same-day delivery” and “24-hr delivery”.
This has spawned a new generation of logistics solutions ranging from the traditional one-on-one equation between the Shipper and Receiver to the complex services that “10PL” logistics providers offer.
Since order-fulfillment is an important driver of Customer Satisfaction, client companies must invest sufficient time and money in assessing which option is best for them and deploy them for best results.
The World Of Modern Logistics and Supply Chain Management
The world of Logistics and Supply Chain Management has become increasingly complex, diverse, and sophisticated. However – since need always necessitates innovation – businesses and logistics companies the world over have scaled new heights of supply chain management to arrive at solutions for modern requirements. Driven by vast advances in modern technology across software, cloud technology, hardware, mobile technology, data analytics (etc) the efficiency and scope of this eco-system have also improved exponentially in recent years.
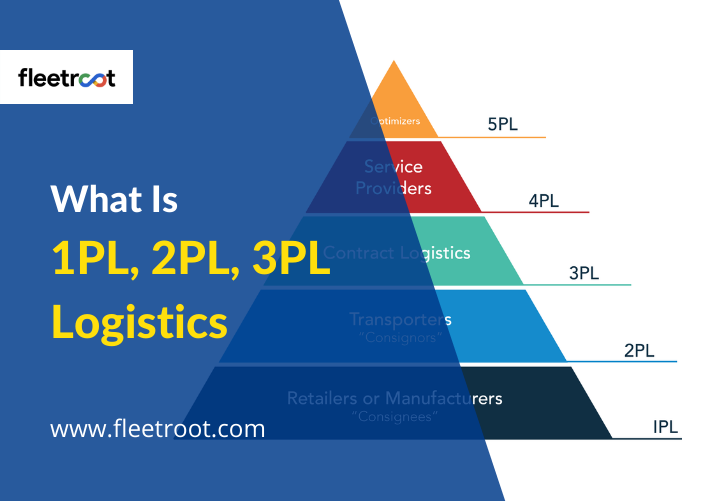
Logistics Services begin with first-party logistics ie 1PL and go up to 10th-party logistics these days. Businesses mostly prefer 3PL, 4PL, and 5PL due to the variety, flexibility, expertise, and economies of scale offered by these providers.
However, the exact roles and responsibilities offered by different logistics providers’ logistics providers and their exact position and area of operation in the supply chain remain unclear for many people.
1PL – 1st Party Logistics
- A company or individual that seeks to transport merchandise (goods, products, cargo etc) moved from its place of origin to another location
- The shipper and receiver of the merchandise are both categorized as 1PL
- 1PL firms are also considered those that do “self-logistics” in the field of commerce
- Eg manufacturer, wholesaler, distributor, retailer, trader, government, importer-exporter
2PL- 2nd Party Logistics
- 2PL execute the movement of cargo by one or more methods of transport (ie road, rail, sea or air) that are part of the larger supply chain
- 2PL are Logistic companies that are often referred to as “those that do the heavy-lifting”. Being the actual “carrier” of goods, they own (or, lease) assets of transport including cargo ships, trains and aircrafts and also enter into exclusive contracts with other companies that own such transport vehicles
- Their forte lies in hauling heavy cargo, large-scale goods over long distances and across international seas and borders and they fulfill the specialized role of moving cargo from one point to another
- 2PL firms often specialize in a particular mode of transport eg Maersk specializes in moving cargo via sea (ships)
- Eg. freight companies (carrying, forwarding), various types of trading and broking companies, export firms, and of course, numerous types of shipping companies
3PL- 3rd Party Logistics
- 3PL is the most popular type of service and is commonly referred to as the “external suppliers” that perform either a part or the entire logistics and supply chain function by integrating services such as receiving, warehousing packaging and shipping
- 3PL companies arrived on the scene during the 1970s decade and they focused on warehousing and transportation. They gradually expanded their operations by offering core services like production and procurement as well as ancillary services such as order fulfillment, packaging, logistics, brokering, forwarding and IT
- Eg. warehouse and distribution, transport, forwarder, shipping, IT, financial
=======================================================
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a 3PL?
3PL: Advantages
- Employ expert logistics professional (instead of internal employees)
- Rapid adoption and usage of new technologies
- Customizable, flexible, nimble (models, resources, SLAs, workforce)
- Economies of scale
- Can grow quickly, add resources and capabilities per requirement, cost can be spread over various clients
3PL: Disadvantages
- Lack of control over your logistics
- Pricing inflexibility, cannot explore various pricing models
- Dependence on provider schedules, lack of autonomy
=========================================================
5PL- 5th Party Logistics
- With the advent of eCommerce businesses the world over, 5PL has become their preferred choice. 5PL providers plan and execute logistics solutions mainly for ecommerce requirements and deal with multiple client companies in offering these solutions (we will visit this topic in greater depth in a future blog)
Last-Mile Delivery and 1PL – 5PL: Must Work Seamlessly Together
We live in a world where “instant gratification” is the norm – everything is cheaper, faster, better, larger, and more. Market innovators like Amazon, Walmart, Uber, Airbnb, and AWS have ushered the “On-Demand Economy” by offering extremely high levels of service and fulfillment such as “24-hr delivery”, “One-hour delivery”, “on-demand server space” while maintaining complete visibility during the entire delivery process.
The old “out for delivery” answer to customers is redundant today. Customer demands rise every day and they know that they will get what they want. If you don’t meet their fulfillment needs to their satisfaction, your competitor will!
But, why is Last-Mile Delivery so important?
Technological diffusion is omnipresent today and one cannot maintain a differential advantage over competition purely on the functional elements of the product. Therefore, Customer Experience becomes all the more important for building loyalty and Last-Mile Delivery is a critical aspect of creating a positive Customer Experience since it is the touch-point between a company and its customers.
The exponential growth of eCommerce businesses has made Last-Mile Delivery even more important since it is the ‘company face’ that consumers see.
1PL- 5PL: Making optimal use of the various service levels of logistics that are now available – from 1PL to 10PL – to manage Last-Mile Delivery is critical. The last-Mile problem is fraught with inefficiency since the last leg of delivery involves multiple stops. Rural areas often have few delivery points that are great distances apart, whereas daily delays of traffic congestion make urban routes equally difficult to negotiate.
Therefore, company leadership must closely investigate the best possible options based on business value-drivers and choose judiciously. This enables companies to optimize their Logistics and Supply Chain from start-to-end ie from the place of origin of their goods to its point of delivery most efficiently and cost-effectively.
Meeting customer fulfillment needs per their expectations regularly will create a positive Customer Experience and result in a loyal customer base and repeatable business.
Modern Logistics Tools: GPS enabled Fleet & Vehicle Tracking Systems
Today’s automated tools such GPS enabled fleet tracking software enable the logistics services providers to efficiently manage and provide the various levels of services (1PL, 3PL, 5PL, etc.) that they offer customers.
Conclusion
Client companies must choose wisely from the available logistics providers and manage their Last Mile Delivery Solution accordingly so that they achieve maximum Customer Satisfaction.